The following resources will help you to tackle the various calculations relating to fractions, decimals and percentages:
Introduction to Fractions - Open University
Finding a Fraction of a Number - Maths Doctor
Simplifying Fractions - Maths Doctor
Learning to multiply fractions efficiently and confidently will help you to work out drug calculations confidently and efficiently. It is absolutely vital to many of the standard formulae used in drug calculations. Thankfully, it is much easier than you probably remember. The screencast below will help you to understand the process. Please do follow the other links available on this site if you are having difficulties with understanding related concepts such as cancelling down. Alternatively, please feel free to book a tutorial or a small group workshop, where I will be able to consolidate your understanding of these calculations.
Multiplying Fractions - Khan Academy
You may need to revise your written division methods from Topic 1 before attempting this section.
Alternatively, it is a very good idea to memorise the most common equivalencies between decimals and fractions so thoroughly that they become second nature to you.
Converting Fractions to Decimals - Khan Academy
Converting Decimals to Fractions - Khan Academy
Fractions, Decimals and Percentages - Khan Academy
Fractions, Decimals and Percentages - Maths Doctor
Once you are confident with all of these, try the test below to check your skills!
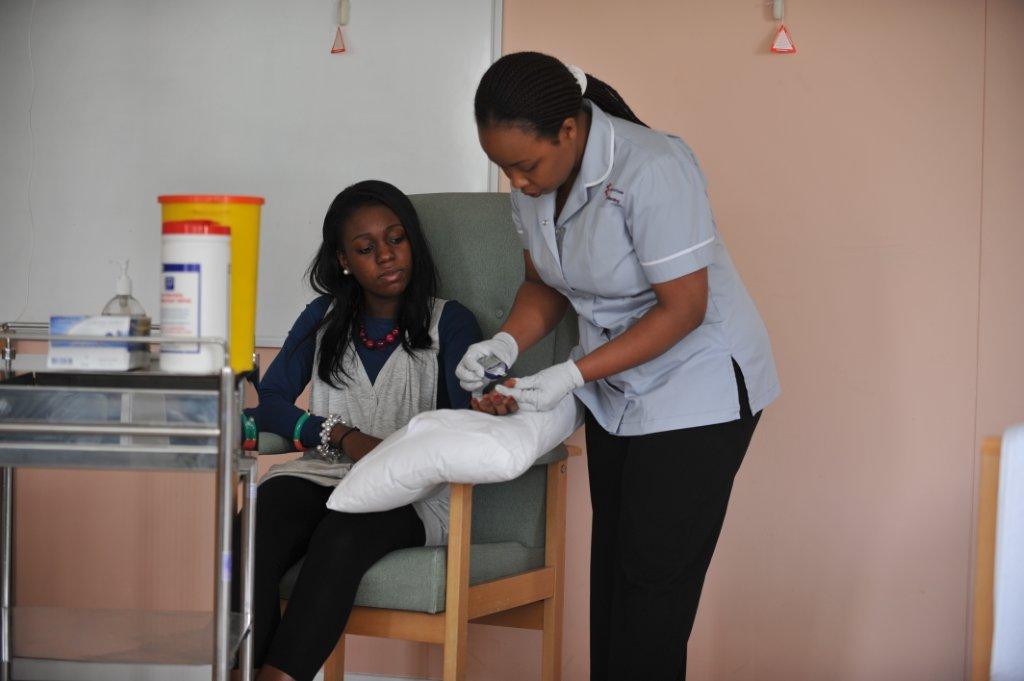 Welcome to the Numeracy Moodle page for the School of Health and Human Sciences.
Welcome to the Numeracy Moodle page for the School of Health and Human Sciences.
 Once you've decided which strategy works best for you, test your skills with this interactive quiz.
Once you've decided which strategy works best for you, test your skills with this interactive quiz. These revision resources contain examples of the type of questions tht you can expect in the Numeracy and Medication Dosage Calculations exam for HS541. Accuracy is essential, and it's important to think about your exam
technique and to be very aware of the areas that you find most
challenging. Remember, these are practise questions only - you may need
to go to the other sections to find tutorial resources to help you to
develop your skills. Alternatively, get in touch with me if you would
like some additional support, either 1:1 or in small groups.
These revision resources contain examples of the type of questions tht you can expect in the Numeracy and Medication Dosage Calculations exam for HS541. Accuracy is essential, and it's important to think about your exam
technique and to be very aware of the areas that you find most
challenging. Remember, these are practise questions only - you may need
to go to the other sections to find tutorial resources to help you to
develop your skills. Alternatively, get in touch with me if you would
like some additional support, either 1:1 or in small groups.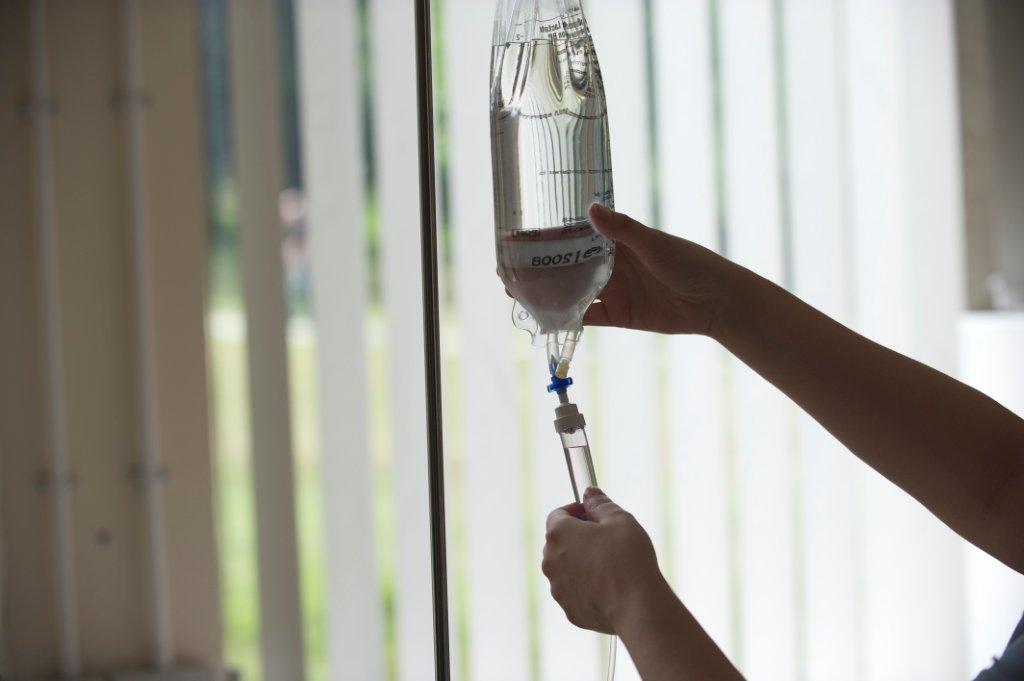  Calculating a flow rate in ml/hr requires us to learn a second formula: Volume = Rate x Time.
Calculating a flow rate in ml/hr requires us to learn a second formula: Volume = Rate x Time.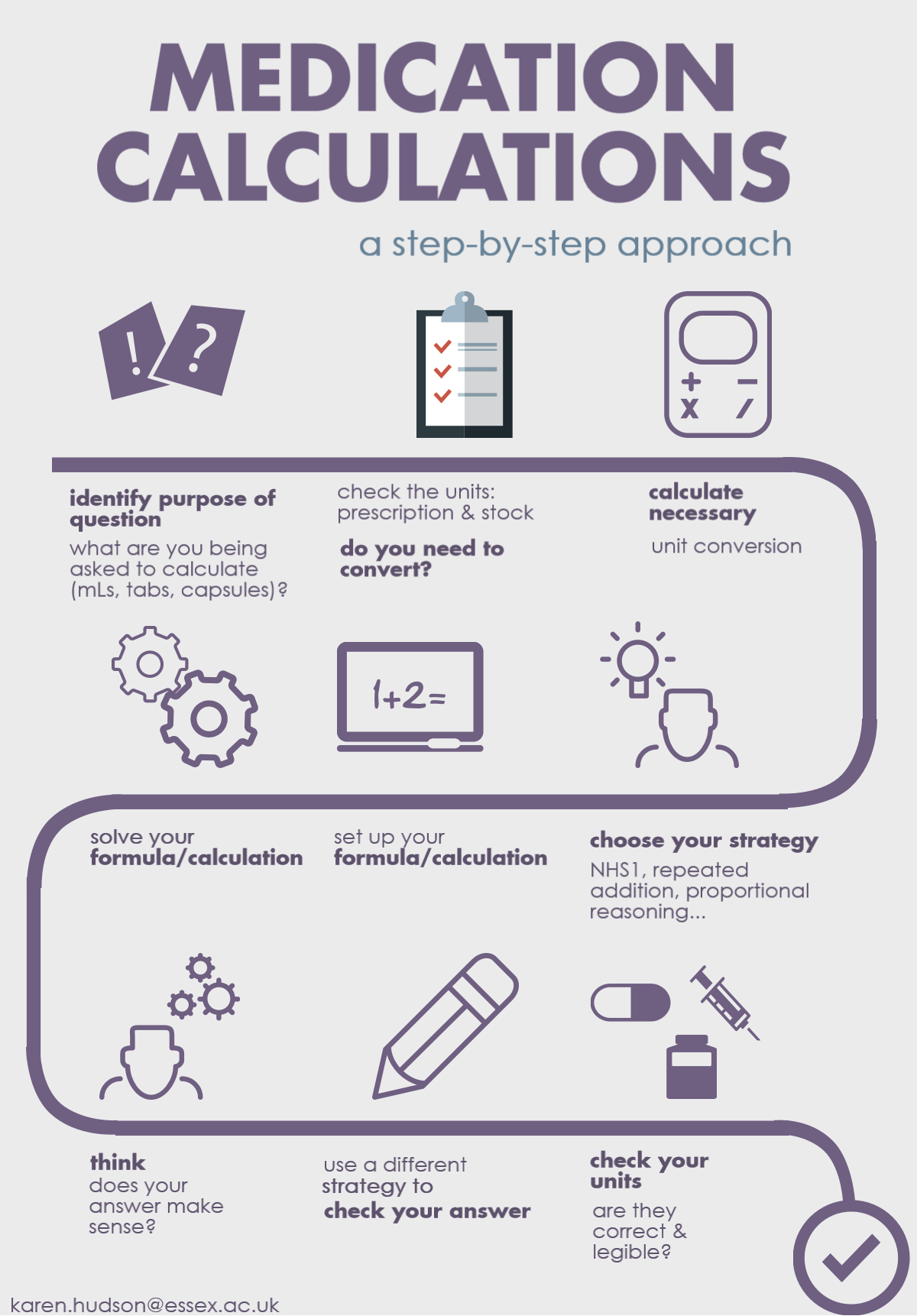 The revision resources below contain examples of the kind of questions you can expect in the Numeracy and Drug Calculations section of the HS563 exam.
The revision resources below contain examples of the kind of questions you can expect in the Numeracy and Drug Calculations section of the HS563 exam.